12 Aug Phlebotomy Medical Terminology You Should Know
Understanding phlebotomy medical terminology is very important if you’re starting or continuing your career in phlebotomy. These words help you every day when you talk to patients, work with other doctors, and learn more about your job. Learning these words helps you explain procedures well, read medical records, and talk clearly with other medical workers. Whether you’re new to phlebotomy or want to know more, knowing these words really helps.
This guide from Phlebotomy Training Specialists will teach you the important words every phlebotomist needs to know. By learning these, you can work better, care for patients better, and grow in your career. Let’s learn about the key terms that help you do your job well.
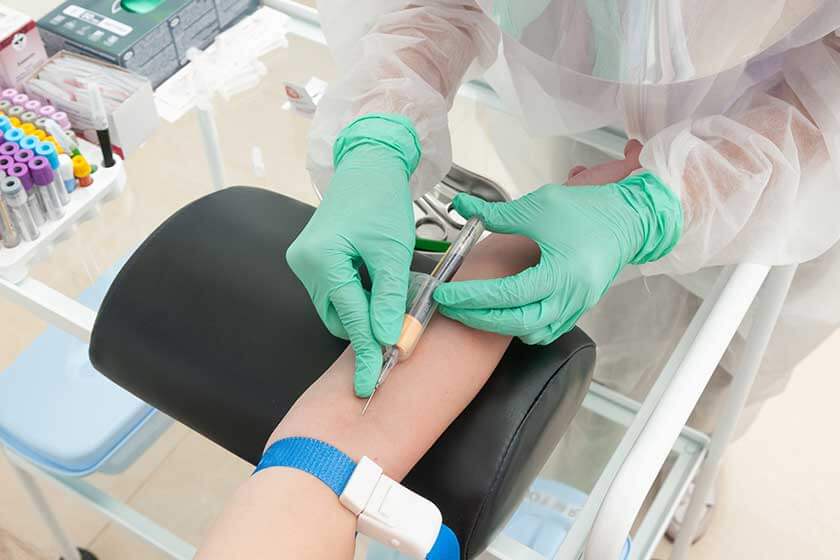
Venipuncture
Venipuncture is a common procedure in which a needle is inserted into a vein, usually in the arm, to collect blood. This is used for many health tests and treatments, like checking for diseases or donating blood.
It’s important to know where the veins are, choose the right one, and use the right method to ensure the patient’s comfort and safety. Venipuncture done well helps patients feel better about the test and ensures the blood sample is good for testing.
Capillary Puncture
Capillary puncture, also called a fingerstick, is used when you need just a little blood or can’t use venipuncture. It’s done by pricking the skin in places like the fingertips or a baby’s heel.
This method is good for quick tests like checking blood sugar in diabetic patients. Since you’re working with smaller blood vessels, knowing how to do it right is important to get a good sample and keep the patient comfortable.
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that keeps blood from clotting. It’s very important in phlebotomy because it helps keep the blood liquid for testing. For example, EDTA keeps blood cells shaped right for certain tests, while heparin is used for tests about blood clotting.
Knowing the different anticoagulants and when to use them ensures the blood samples are handled correctly.
Hemolysis
Hemolysis occurs when red blood cells break apart, which can mess up test results. To prevent this, it’s important to use the right needle size and method.
Knowing how to avoid hemolysis helps make sure the blood tests are correct and reliable.
Serum vs. Plasma
Knowing the difference between serum and plasma is important because they are used for different tests. Plasma comes from blood that has anticoagulants and includes clotting factors, while serum is what you get after blood has clotted and the clot is removed.
Phlebotomists need to handle each sample type correctly to ensure tests are accurate.
Edema
Edema occurs when fluid builds up in the tissues, causing swelling. Drawing blood from that area can be difficult if someone has edema.
Phlebotomists need to know how to find the best place for a blood draw when there’s edema to ensure the sample is good and the patient is comfortable.
Fasting Specimen
Some tests, like those for blood sugar or cholesterol, require a fasting specimen, which means the patient should not eat or drink anything but water for 8-12 hours before the test.
It’s your job to ensure patients know and follow these rules to ensure their test results are right.
Chain of Custody
The chain of custody is important when blood tests can affect legal decisions, like drug testing. This process tracks the sample from when it’s collected until it’s tested.
Phlebotomists must follow this process closely to ensure the test results are valid.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a yellow compound produced by the breakdown of red blood cells and processed by the liver. High levels can indicate liver problems.
Tests for bilirubin need special care because light can change the results. Samples must be protected from light and handled quickly.
Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a tool that spins blood to separate it into different parts, like plasma and red blood cells, for testing.
Knowing how to use a centrifuge safely and correctly is important for getting accurate test results.
Aseptic Technique
By learning and using all these skills and knowledge from Phlebotomy Training Specialists, you can do your job well and help many people with their health care. Our courses teach you everything you need to know so you’re ready for real situations in the medical field. With our help, you’ll be able to meet the challenges of the healthcare world and move forward in your phlebotomy career.
